初探MCP server
这里参考 https://modelcontextprotocol.io/quickstart/server 运行一个简单的MCP Server, 并在本地客户端(Cursor)里调用它
大部分 LLM 目前无法获取实时的天气预报,例如:

使用 MCP 可以解决这个问题,我们将构建一个MCP server,它公开两个工具:get-alerts 和 get-forecast。然后,我们将LLM连接到 MCP server。
MCP Server可提供三种主要功能:
- 资源(Resources):客户端可读取的类文件数据(例如 API 响应或文件内容)
- 工具(Tools):LLM 可调用的函数
- 提示(Prompts):帮助用户完成特定任务的预编写模板
本节我们关注Tools
部署weather MCP
访问以下文件,将其内容复制到本地的一个py文件:
安装依赖:
pip3 install httpx mcp-python

这里我们使用cursor来访问MCP server,打开Cursor右上角的设置,然后找到MCP:
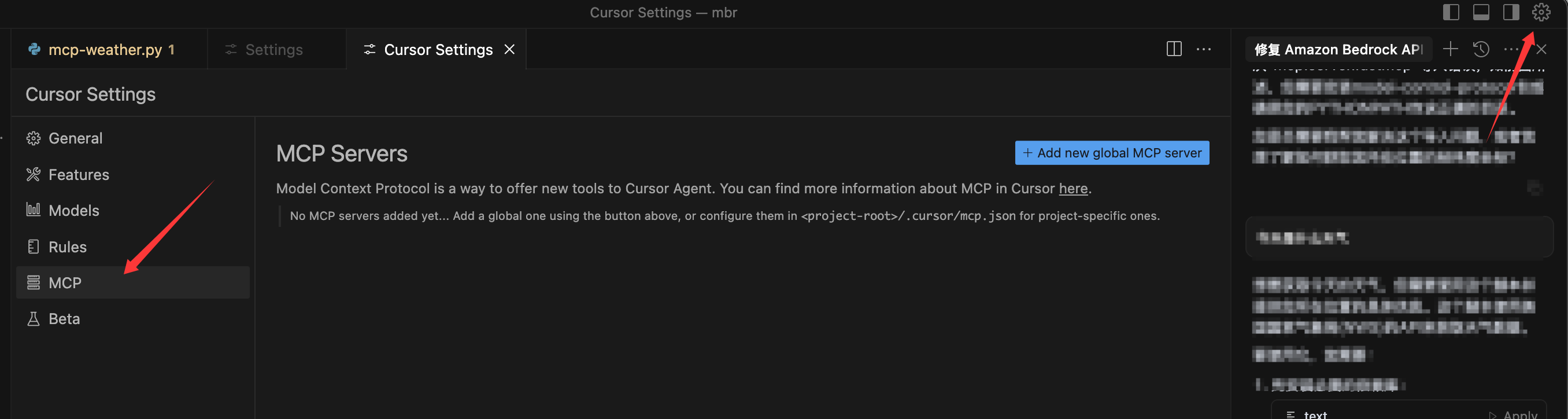
点击Add new global MCP server,会进入一个json的编辑页面,其实这个json保存在这个目录:
cat ~/.cursor/mcp.json
{
"mcpServers": {}
}
这个配置是全局生效的,如果只要对当前项目生效,就在当前目录创建并编辑mcp.json。
将这个内容编辑为如下,注意替换实际的python路径以及上面的py文件路径:
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "/opt/homebrew/bin/python3.12",
"args": [
"/Users/kpingfan/code/xxx/mcp-weather.py"
]
}
}
}
编辑完成后的效果:

此时回到cursor setting页面,发现状态是绿色,如果配置错误,比如python文件路径错误,则会显示具体的报错:

在cursor里进行提问,能看到调用MCP tool的记录:

对MCP Server进行调试
运行:
mcp dev mcp-weather.py
这个命令会提示MCP Inspector运行在6274端口:

然后浏览器访问对应链接,打开MCP Inspector页面,在里面输入command和arguments,点击连接。在Tools页面,点击List tools,发现里面有两个tool:

调试get_alerts这个tool,输入一个state缩写,点击Run Tool后,会返回相关结果:

在底部的history页面,能够看到更详细的请求和返回:

附
上面demo的python代码如下(2025.04.20):
from typing import Any
import httpx
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("weather")
# Constants
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
async def make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""Format an alert feature into a readable string."""
props = feature["properties"]
return f"""
Event: {props.get('event', 'Unknown')}
Area: {props.get('areaDesc', 'Unknown')}
Severity: {props.get('severity', 'Unknown')}
Description: {props.get('description', 'No description available')}
Instructions: {props.get('instruction', 'No specific instructions provided')}
"""
@mcp.tool()
async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
"""Get weather alerts for a US state.
Args:
state: Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
"""
url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
data = await make_nws_request(url)
if not data or "features" not in data:
return "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found."
if not data["features"]:
return "No active alerts for this state."
alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in data["features"]]
return "\n---\n".join(alerts)
@mcp.tool()
async def get_forecast(latitude: float, longitude: float) -> str:
"""Get weather forecast for a location.
Args:
latitude: Latitude of the location
longitude: Longitude of the location
"""
# First get the forecast grid endpoint
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(points_url)
if not points_data:
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location."
# Get the forecast URL from the points response
forecast_url = points_data["properties"]["forecast"]
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return "Unable to fetch detailed forecast."
# Format the periods into a readable forecast
periods = forecast_data["properties"]["periods"]
forecasts = []
for period in periods[:5]: # Only show next 5 periods
forecast = f"""
{period['name']}:
Temperature: {period['temperature']}°{period['temperatureUnit']}
Wind: {period['windSpeed']} {period['windDirection']}
Forecast: {period['detailedForecast']}
"""
forecasts.append(forecast)
return "\n---\n".join(forecasts)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport='stdio')
通过阅读以上代码, 我们发现:
@mcp.tool()关键字用来暴露tools, 例如get_forecast函数- Tools函数里的注释非常关键,它告诉MCP Client如何调用它,例如
Get weather forecast for a location.,这和langchain的工作模式非常像。 - MCP Servers代码运行在用户自己的电脑里,它作为中间人,向远端的服务发送请求